In the world of modern networking, there are two technologies that are always looked at in the Philippines: Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) and Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS). Both technologies offer benefits that can help businesses improve their network performance and reduce costs. However, they differ in terms of functionality, cost, and ease of use. In this article, we will explore the differences between SD-WAN vs MPLS and help you decide which one is best for your business.
What is SD-WAN?

SD-WAN is a software-defined networking technology that allows organizations to build a secure, intelligent, and scalable WAN using a combination of public and private connectivity. With it, organizations can use multiple Internet connections, including broadband, LTE, and MPLS, to connect their branch offices, data centers, and cloud resources.
It enables centralized network management and control, which simplifies network operations and improves agility. It uses software to dynamically route traffic across multiple links based on business policies, network conditions, and application requirements. SD-WAN also provides advanced security features such as encrypted tunnels, firewalls, and intrusion prevention.
What is MPLS?

MPLS is a networking technology that uses labels to forward packets instead of traditional IP routing. It creates a virtual circuit or tunnel between two endpoints, allowing data to be transmitted faster and more securely. It is often used in large enterprises that require a high level of network reliability and performance.
MPLS is a managed service, which means that service providers are responsible for managing and maintaining the network. MPLS provides QoS (Quality of Service) guarantees, which means that applications can be prioritized, and bandwidth can be reserved for critical applications. MPLS is also a private network, which provides a higher level of security than the public Internet.
SD-WAN vs MPLS Comparison

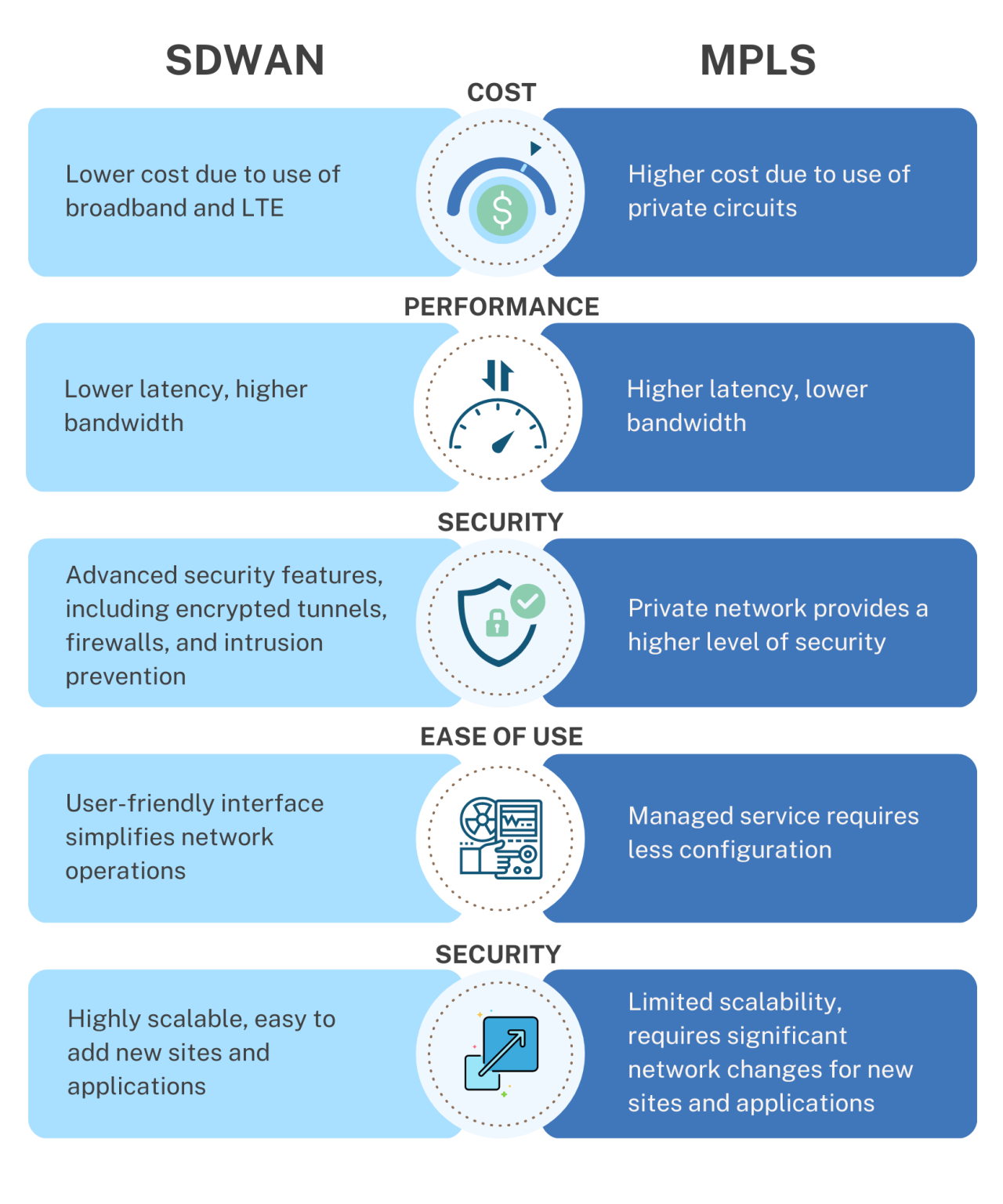
Cost Comparison

SD-WAN is typically less expensive than MPLS because it uses broadband and LTE connections instead of private circuits. SD-WAN also allows organizations to prioritize traffic and allocate bandwidth based on application requirements, which can further reduce costs. MPLS is a managed service, which means that service providers are responsible for managing and maintaining the network, but this can also add to the cost.
Performance Comparison

SD-WAN typically provides lower latency and higher bandwidth than MPLS because it uses multiple Internet connections. SD-WAN can dynamically route traffic across multiple links based on business policies and network conditions, which can improve performance. MPLS provides QoS guarantees, which means that applications can be prioritized, and bandwidth can be reserved for critical applications.
Security Comparison

SD-WAN provides advanced security features such as encrypted tunnels, firewalls, and intrusion prevention, which can help protect against cyber threats. MPLS provides a higher level of security than the public Internet because it is a private network.
Ease of Use Comparison

SD-WAN provides a user-friendly interface that simplifies network operations and improves agility. SD-WAN allows organizations to prioritize traffic and allocate bandwidth based on application requirements, which can reduce complexity. MPLS is a managed service, which requires less configuration, but can also limit flexibility and scalability.
Benefits and Uses of SD-WAN and MPLS

So how do businesses know when to use one or the other? This all depends on the situation and unique challenges businesses need to solve. Below are a few benefits that SD-WAN can provide businesses:
- Lower cost due to use of broadband and LTE connections.
- Higher performance due to use of multiple Internet connections.
- Advanced security features, including encrypted tunnels, firewalls, and intrusion prevention.
- User-friendly interface that simplifies network operations and improves agility.
- Highly scalable, easy to add new sites and applications.
Some use cases in which SD-WAN are a good choice are:
- Have multiple locations and need to connect them.
- Need to improve network performance and reduce latency.
- Want to reduce network costs by using broadband and LTE connections.
- Need to prioritize traffic and allocate bandwidth based on application requirements.
- Want to simplify network operations and improve agility.
Alternatively, MPLS benefits would be:
- Higher level of security due to use of private network.
- QoS guarantees, which means that applications can be prioritized, and bandwidth can be reserved for critical applications.
- Managed service requires less configuration, which can reduce complexity.
- Provides a reliable and stable network for mission-critical applications.
- Offers end-to-end network performance monitoring and reporting.
Some use cases for MPLS are:
- Have a high level of network security requirements.
- Need to guarantee QoS for critical applications.
- Have a need for a stable and reliable network for mission-critical applications.
- Have a need for end-to-end network performance monitoring and reporting.
- Require a managed service that requires less configuration.
FAQ's
Can SD-WAN be used in conjunction with MPLS?
Yes, SD-WAN can be used to augment or replace MPLS in certain scenarios, such as adding redundancy or reducing costs.
Is MPLS still relevant in today’s networks?
Yes, MPLS is still widely used in large enterprises and service provider networks due to its reliability, security, and QoS guarantees.
Can SD-WAN be deployed on a global scale?
Yes, SD-WAN can be deployed globally, but organizations should consider factors such as Internet connectivity, local regulations, and data sovereignty.
What are some common use cases for SD-WAN?
Common use cases for SD-WAN include branch office connectivity, cloud connectivity, and mobile workforce connectivity.
How can I determine which technology is best for my organization?
Organizations should evaluate their specific requirements and needs, including performance, security, cost, and scalability, to determine which technology is best for their network. Consulting with a network expert can also help in making an informed decision.

